Let’s face it; generating solar energy is great! But what impact does the growing number of residences with solar panels on their roofs have on the electrical grid? First of all, solar power helps reduce the need for electricity otherwise generated by fossil fuels. Now, who wouldn’t want to help cut greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change? There appears to be a list of individuals and organizations.
Clearly a number of sceptics argue that the electrical grid can’t handle the expansion of solar power and that overwhelmed utility companies and energy providers will need to invest massive amounts of money in upgrading their infrastructure that will drive the cost of energy up for the consumer. If you take their word for it, that doesn’t sound like the promised future of clean and cheap energy. But is there some truth in there? Like all stories, this could vaguely be based on some kind of truth, because managing the electrical grid, is definitely not an easy task. Let’s explore this further and discuss how you, as a consumer, can contribute to the solution.
Utility companies need to make sure there is adequate electricity available to meet demand at all hours of the day and night. They are in charge of power generation, transmission, and distribution. Utility companies must also ensure that any excess electricity is used or stored somewhere. Excessive electricity can produce frequency variations, which can cause damage, fires, and blackouts. This is why there are massive international forecasts on energy demand and production. ENTSO-E is such an organization. Forecasts and actual data on load, generation, pricing, and so on can be found on their website.
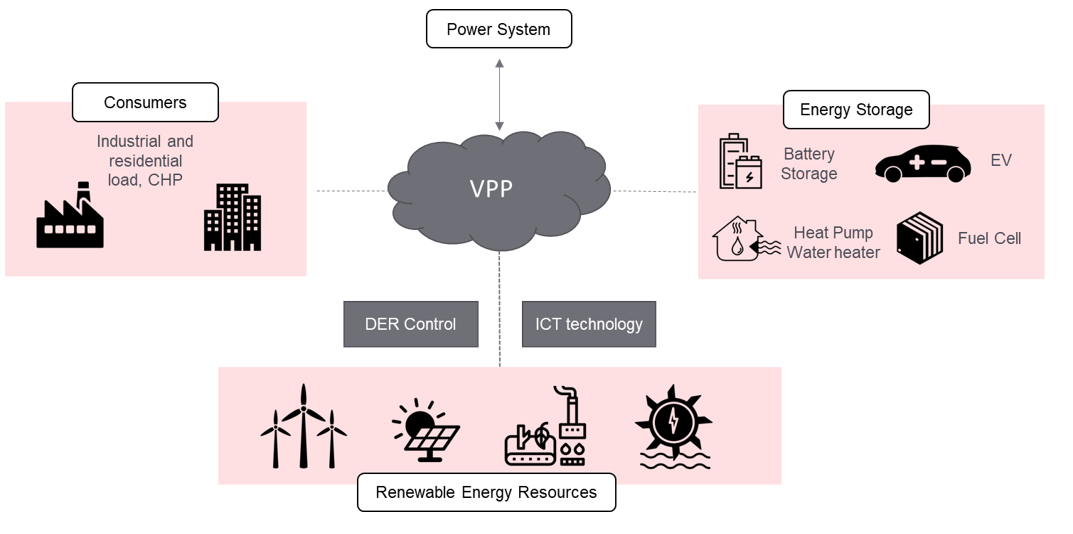
So, what does any of this have to do with the title’s reference to Virtual Power Plants? VPPs are a relatively new type of energy infrastructure that connects distributed energy resources (DERs) from several thousands of households and businesses into a single virtual network. VPPs use sophisticated software to talk to each other to manage and optimize the energy production and consumption of various DERs in real time, allowing them to function as a single organism that responds to the needs of the grid. This means that if the grid experiences a spike in energy demand that cannot be met, the combined resources scattered over thousands of homes and businesses can step in and meet that demand. When there is an unanticipated surplus, the utility company can use the VPP’s battery network to store that electricity or shift it to another location with a known demand.
But why does this matter?
VPPs are increasingly playing a pivotal role in the way we generate, consume, and manage energy. To understand the significance of these systems, let’s delve into four key reasons why they are truly matter.
Increased grid efficiency
VPPs help to maximize the use of renewable energy resources by coordinating the output of different distributed energy resources (DERs). For example, if there is excess solar power being generated in one location, that power can be distributed to other locations in the network where there is a shortfall. VPPs ensure that the energy system operates at peak efficiency by balancing the output of various energy sources in real time.
 Source: futurebridge
Source: futurebridge
Furthermore, VPPs help to prevent energy waste by storing extra energy created during low demand periods for eventual usage during peak demand periods. A VPP may store extra solar power generated throughout the day in batteries and then use that electricity to fulfill nighttime peak demand.
VPPs also help to optimize the use of energy by coordinating the consumption of energy resources in real-time. For example, a VPP could use advanced software algorithms to schedule the use of energy-intensive appliances like electric vehicles or heating systems to avoid periods of high demand and reduce strain on the grid.
Cost savings
VPPs help to reduce the total cost of energy production by reducing the need for costly upgrades to current grid infrastructure. They ensure a stable and predictable power supply, outperforming conventional fossil-fuelled power plants in terms of efficiency. This is achieved through the coordination and balancing of output from multiple Distributed Energy Resources (DERs), thus lessening the necessity for high-cost peaking power facilities often used to satisfy peak energy demands. In contrast to traditional power plants, which require a significantly extended response time to cater to unexpected peak demand, VPPs are much more agile.
These advantages will help to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy system without breaking the bank.
Increased reliability
Another key advantage of VPPs is their potential to improve energy system reliability. VPPs provide a consistent and reliable power source by balancing the output of several energy sources in real time. This helps to reduce the impact of changes in energy supply or demand and provide users with a more steady and consistent source of power.
By integrating a range of various energy sources into a single network, VPPs serve to lessen the impact of energy supply disruptions. If one wind turbine or solar panel fails, for example, the VPP can compensate by taking electricity from other sources in the network. This helps to lower the likelihood of blackouts or power disruptions. If there are power outages, VPPs can offer backup power with a reliable source of power during times of peak demand or in the case of an interruption in the energy supply by storing extra energy produced during times of low demand.
By lowering the possibility of voltage and frequency fluctuations, VPPs contribute to the grid’s stability. This gives the grid a more reliable and constant source of power by coordinating the output of various DERs, therefore lowering the chances of those harmful voltage and frequency variations.
Overall, by improving the reliability of the energy system, VPPs help to ensure that consumers have access to a stable and consistent source of power.
Environmental benefits
VPPs have the potential to improve the environment by promoting the use of renewable energy sources, which is a substantial additional advantage. By combining and coordinating their production, VPPs support the use of renewable energy sources including wind, solar, and hydro power. They can contribute to reducing the damaging effects of conventional fossil-fueled power plants on the environment by encouraging the use of clean energy sources.
VPPs offer a more effective and affordable means of fulfilling energy demand, hence reducing the need for conventional fossil-fueled power plants. They can facilitate the integration of Electric Vehicles (EVs) by, among other things, offering a mechanism to control and optimize their charging and discharging. This helps to reduce the strain on the grid during periods of high demand and maximize the use of renewable energy sources.
By boosting the use of renewable energy sources and decreasing the reliance on fossil fuel-powered power plants, VPPs contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. They can and are speeding up the transition to a more sustainable energy system that is better prepared to handle the challenges of climate change by encouraging the use of clean energy.
Current state of VPPs
Now if you’re wondering how to get into the VPP game, you can join a Virtual Power Plant program today depending on the hardware you have and where you live. For example, Tesla launched a VPP test in 2021 for Powerwall owners living in Australia and California. This program has expanded since then and starting last summer, those owners are (finally) getting paid for their contributions to the VPP. For our readers in Europe, rest assured, there are similar opportunities available as well such as:
A great example of what a VPP could look like, is this neighborhood in Ghent(BE) De Nieuwe Dokken, it was built with a VPP approach in mind, which consists of 400 homes, a school and some businesses. They started off with 20 EV chargers, 80kWp of solar panels, a 240kWh neighborhood battery, district heat, a massive collective heat pump that reuses residual heat from the neighborhood’s wastewater.
In general, VPPs (will) contribute to the development of a more ecologically friendly and sustainable energy system by encouraging the use of renewable energy sources and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This by addressing the challenges caused by climate change and building a more durable and sustainable energy future for generations to come.